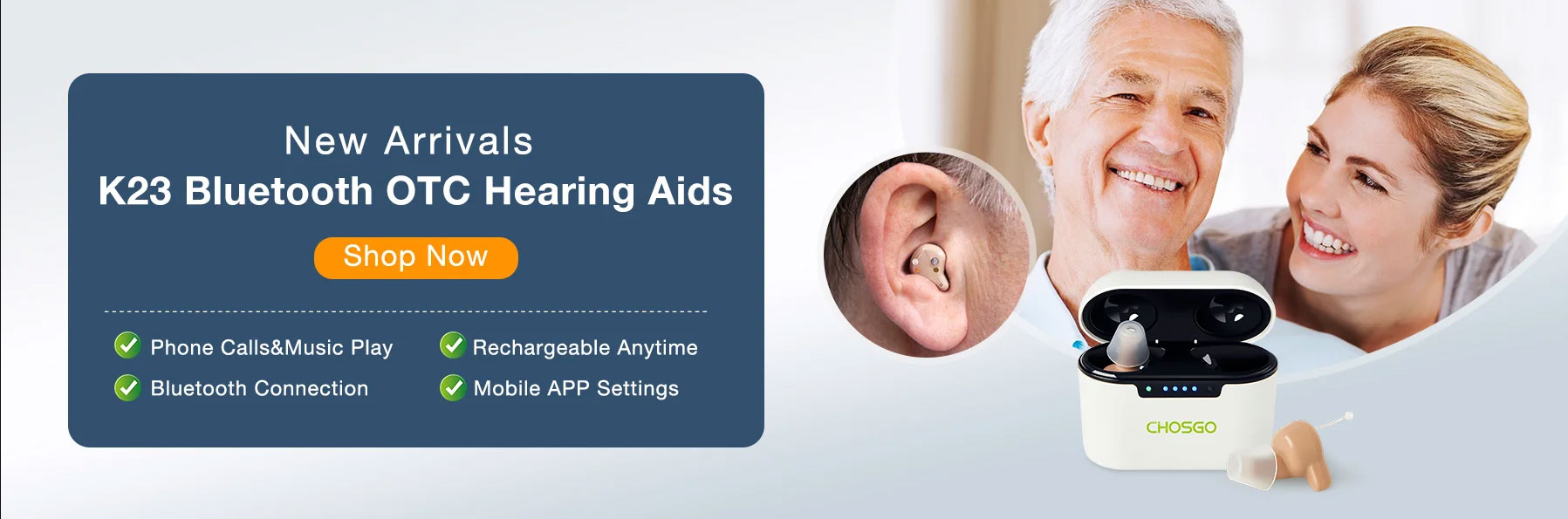
what does it mean your left ear itches
- Date:
- Views:13
BROWSING THE GLOBE OF ICD-10 CODING FOR HEARING LOSS: A COMPREHENSIVE OVERVIEW
Hearing loss, a widespread problem impacting people of every ages and histories, can profoundly impact interaction, social communication, and general lifestyle. Accurate medical diagnosis and coding of hearing loss are vital for guaranteeing appropriate health care distribution, invoicing, and research. This detailed overview explores the numerous aspects of hearing loss and supplies a thorough evaluation of the applicable ICD-10 coding system.
Hearing loss, additionally referred to as hearing impairment, occurs when the ear is not able to find or refine sound waves effectively. This can be because of numerous aspects that affect different parts of the acoustic system, consisting of the outer ear, center ear, inner ear, or acoustic nerve. The different kinds of hearing loss include conductive hearing loss, sensorineural hearing loss, and blended hearing loss.
Impediment in acoustic understanding: This classification includes problems with the external or center ear, obstructing sound waves from accessing the inner ear.
Sensorineural hearing loss: This kind emerges from injury or malfunctioning of the inner ear or the acoustic nerve.
Responsible for translating sound waves into electric signals for the brain to recognize.
Certain variables can add to sensorineural hearing loss, including age-related hearing decline (presbycusis), direct exposure to loud noises, and specific medicines.
Mix hearing loss: This classification integrates the qualities of conductive and sensorineural hearing loss, resulting in an unique hearing account.
The Importance of Accurate Coding
Precise and consistent coding of listening to loss using the International Classification of Conditions. Tenth Modification (ICD-10) is necessary for several motives:
Clear and efficient interaction is improved by utilizing accurate codes when interacting among doctor, insurer, and public health organizations.
Compensation: Accurate coding guarantees the appropriate invoicing. Settlement for health care solutions connected to listening to loss assessment, treatment, and recovery.
Reliable analytical compilation is important for study and analysis in the field of listening to loss. Constant coding allows the development of an extensive data source that can be used to analyze the prevalence, creates, treatment results, and numerous facets of hearing impairment. This, consequently, allows for a deeper understanding of the concern and informs the advancement of efficient interventions and services.
Listening To Loss ICD-10 Codes
The ICD-10 coding system arranges numerous health problems and clinical diagnoses, which also consists of hearing loss. Below is a summary of the pertinent codes for hearing loss.
H90: Hearing loss: This essential class encompasses numerous designs of hearing loss.
Laterality: The first number complying with H90 defines the laterality, whether or not the paying attention to loss is:
0: Reciprocal (influencing each ear)
1: Independent (impacting one ear)
2: Not specified (unknown side)
Type of Hearing Loss: The 2d figure identifies the specific type of paying attention loss:
"no Conductivity: A Study"
3 sorts of Sensorineural hearing loss
6: Combination of Conductive and Sensorineural Hearing Loss
For a 70-year-old person experiencing reciprocal, recurring sensorineural hearing loss because of presbycusis, the suitable code would be H90.3.1.
A younger grown-up artist reports unexpected listening to loss in a solitary ear complying with publicity to loud songs at a real-time performance. The code could be H90.4.0 (severe unilateral sensorineural listening to loss) with a feasible additional code for noise-triggered hearing loss (T70.5).
A senior person that has had ear infections in the past is experiencing a decrease in hearing in both ears. Upon analysis, the doctor diagnoses reciprocal conductive hearing loss due to recurring otitis media. The equivalent codes could be H90.0.1 for persistent reciprocal conductive hearing loss and H65.9 for unspecified otitis media.
Choosing the Correct Code
Picking the maximum correct ICD-10 code. For every instance requires cautious consideration. Health care professionals need to inquire from appropriate coding referrals and sources. That include the ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines. The American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery (AAO-HNS) Coding Companion.
Additional Aspects to Think About in ICD-10 Coding for Hearing Loss
Degree of Extent: Although it is not particularly resolved in the primary ICD-10 codes, certain medical care companies might utilize supplemental coding systems such as V codes to indicate the level of hearing loss (moderate, modest, extreme, extensive).
Etiology: Identifying the underlying function of paying attention to loss is crucial for treatment and can be captured using additional ICD-10 codes special to the causative situation (e.g., H65.Nine for otitis media, T70.5 for noise-caused hearing loss).
Common Comorbidities: Hearing loss frequently co-occurs with various other health and wellness problems, such as ringing in the ears (a buzzing experience in the ears) or balance difficulties. These associated conditions can be noted utilizing appropriate ICD-10 codes.
Future Growths and Difficulties in ICD-11
While ICD-10 acts as the present requirement for scientific coding in several countries, the Globe Health And Wellness Company (THAT) has actually developed ICD-11, with an execution target of January 1, 2027.
Here's a look into possible changes regarding hearing loss coding in ICD-11:
Improved Specificity: ICD-11 can likewise present extra one-of-a-kind codes for many types and reasons for hearing loss, potentially boosting precision and facilitating studies on specific subgroups of the population.
Extent Assimilation: The incorporation of severity degrees within the primary for listening to loss in ICD-11 removes the need for added coding systems such as V codes.
Highlight Practical Effects: The ingenious device may concentrate more on the meaningful influence of hearing loss on daily life, thinking about an extra extensive recording of the patient's experience.
Nevertheless, imposing ICD-eleven additionally provides obstacles:
Transitional Obstacles: Changing to a new coding gadget require large education and learning and variant for health care experts, incurring ability fees and disruption during the transition length.
Compatibility and Interoperability: Ensuring very easy details change between health care facilities the use of remarkable variants of the coding gadget calls for mindful planning and execution strategies.
Verdict
To conclude, knowledge and utilizing ICD-10 codes successfully is important for appropriate communique, proper repayment, and trustworthy stats concerning hearing loss. As the health care view progresses, staying well-informed regarding the renovation and capability implementation of ICD-eleven might be very important for health care specialists involved in handling dealing with listening to loss sufferers. By embracing ongoing developments in coding systems while making certain exact and regular execution of present methods, we can add to enhancing the overall fine of care for individuals with hearing loss.
Best OTC Hearing Aids hearing aids near me hearing aids online hearing test
Hearing loss, a widespread problem impacting people of every ages and histories, can profoundly impact interaction, social communication, and general lifestyle. Accurate medical diagnosis and coding of hearing loss are vital for guaranteeing appropriate health care distribution, invoicing, and research. This detailed overview explores the numerous aspects of hearing loss and supplies a thorough evaluation of the applicable ICD-10 coding system.
Hearing loss, additionally referred to as hearing impairment, occurs when the ear is not able to find or refine sound waves effectively. This can be because of numerous aspects that affect different parts of the acoustic system, consisting of the outer ear, center ear, inner ear, or acoustic nerve. The different kinds of hearing loss include conductive hearing loss, sensorineural hearing loss, and blended hearing loss.
Impediment in acoustic understanding: This classification includes problems with the external or center ear, obstructing sound waves from accessing the inner ear.
Sensorineural hearing loss: This kind emerges from injury or malfunctioning of the inner ear or the acoustic nerve.
Responsible for translating sound waves into electric signals for the brain to recognize.
Certain variables can add to sensorineural hearing loss, including age-related hearing decline (presbycusis), direct exposure to loud noises, and specific medicines.
Mix hearing loss: This classification integrates the qualities of conductive and sensorineural hearing loss, resulting in an unique hearing account.
The Importance of Accurate Coding
Precise and consistent coding of listening to loss using the International Classification of Conditions. Tenth Modification (ICD-10) is necessary for several motives:
Clear and efficient interaction is improved by utilizing accurate codes when interacting among doctor, insurer, and public health organizations.
Compensation: Accurate coding guarantees the appropriate invoicing. Settlement for health care solutions connected to listening to loss assessment, treatment, and recovery.
Reliable analytical compilation is important for study and analysis in the field of listening to loss. Constant coding allows the development of an extensive data source that can be used to analyze the prevalence, creates, treatment results, and numerous facets of hearing impairment. This, consequently, allows for a deeper understanding of the concern and informs the advancement of efficient interventions and services.
Listening To Loss ICD-10 Codes
The ICD-10 coding system arranges numerous health problems and clinical diagnoses, which also consists of hearing loss. Below is a summary of the pertinent codes for hearing loss.
H90: Hearing loss: This essential class encompasses numerous designs of hearing loss.
Laterality: The first number complying with H90 defines the laterality, whether or not the paying attention to loss is:
0: Reciprocal (influencing each ear)
1: Independent (impacting one ear)
2: Not specified (unknown side)
Type of Hearing Loss: The 2d figure identifies the specific type of paying attention loss:
"no Conductivity: A Study"
3 sorts of Sensorineural hearing loss
6: Combination of Conductive and Sensorineural Hearing Loss
For a 70-year-old person experiencing reciprocal, recurring sensorineural hearing loss because of presbycusis, the suitable code would be H90.3.1.
A younger grown-up artist reports unexpected listening to loss in a solitary ear complying with publicity to loud songs at a real-time performance. The code could be H90.4.0 (severe unilateral sensorineural listening to loss) with a feasible additional code for noise-triggered hearing loss (T70.5).
A senior person that has had ear infections in the past is experiencing a decrease in hearing in both ears. Upon analysis, the doctor diagnoses reciprocal conductive hearing loss due to recurring otitis media. The equivalent codes could be H90.0.1 for persistent reciprocal conductive hearing loss and H65.9 for unspecified otitis media.
Choosing the Correct Code
Picking the maximum correct ICD-10 code. For every instance requires cautious consideration. Health care professionals need to inquire from appropriate coding referrals and sources. That include the ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines. The American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery (AAO-HNS) Coding Companion.
Additional Aspects to Think About in ICD-10 Coding for Hearing Loss
Degree of Extent: Although it is not particularly resolved in the primary ICD-10 codes, certain medical care companies might utilize supplemental coding systems such as V codes to indicate the level of hearing loss (moderate, modest, extreme, extensive).
Etiology: Identifying the underlying function of paying attention to loss is crucial for treatment and can be captured using additional ICD-10 codes special to the causative situation (e.g., H65.Nine for otitis media, T70.5 for noise-caused hearing loss).
Common Comorbidities: Hearing loss frequently co-occurs with various other health and wellness problems, such as ringing in the ears (a buzzing experience in the ears) or balance difficulties. These associated conditions can be noted utilizing appropriate ICD-10 codes.
Future Growths and Difficulties in ICD-11
While ICD-10 acts as the present requirement for scientific coding in several countries, the Globe Health And Wellness Company (THAT) has actually developed ICD-11, with an execution target of January 1, 2027.
Here's a look into possible changes regarding hearing loss coding in ICD-11:
Improved Specificity: ICD-11 can likewise present extra one-of-a-kind codes for many types and reasons for hearing loss, potentially boosting precision and facilitating studies on specific subgroups of the population.
Extent Assimilation: The incorporation of severity degrees within the primary for listening to loss in ICD-11 removes the need for added coding systems such as V codes.
Highlight Practical Effects: The ingenious device may concentrate more on the meaningful influence of hearing loss on daily life, thinking about an extra extensive recording of the patient's experience.
Nevertheless, imposing ICD-eleven additionally provides obstacles:
Transitional Obstacles: Changing to a new coding gadget require large education and learning and variant for health care experts, incurring ability fees and disruption during the transition length.
Compatibility and Interoperability: Ensuring very easy details change between health care facilities the use of remarkable variants of the coding gadget calls for mindful planning and execution strategies.
Verdict
To conclude, knowledge and utilizing ICD-10 codes successfully is important for appropriate communique, proper repayment, and trustworthy stats concerning hearing loss. As the health care view progresses, staying well-informed regarding the renovation and capability implementation of ICD-eleven might be very important for health care specialists involved in handling dealing with listening to loss sufferers. By embracing ongoing developments in coding systems while making certain exact and regular execution of present methods, we can add to enhancing the overall fine of care for individuals with hearing loss.
Best OTC Hearing Aids hearing aids near me hearing aids online hearing test